What is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
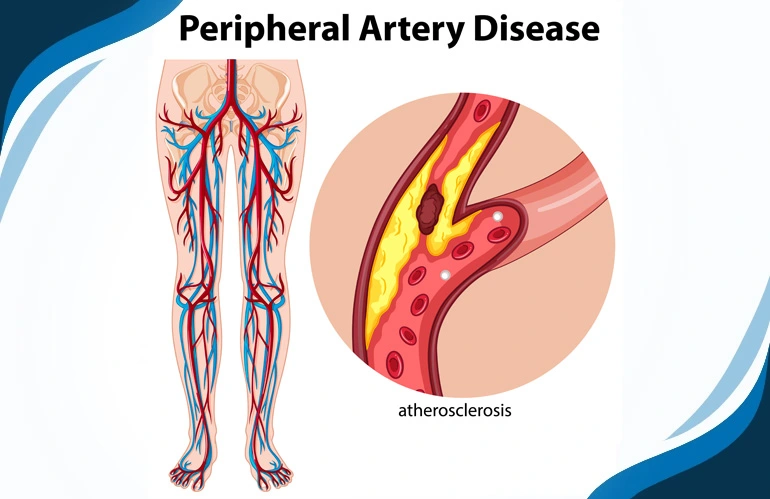
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a vascular condition characterized by the narrowing or blockage of arteries that supply blood to the extremities, primarily the legs. It is a type of peripheral vascular disease that results from atherosclerosis, a process in which fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the arterial walls, forming plaques.

What causes PAD and who is at risk?
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances on the inner walls of arteries. The formation of plaques narrows and restricts blood flow to the extremities, most commonly affecting the legs. Several factors contribute to the development of PAD, and certain individuals are at a higher risk.
Here are key causes and risk factors:
Causes:
- Atherosclerosis: The leading cause of PAD is atherosclerosis, the accumulation of plaque in the arteries. Over time, this process can result in the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels.
Risk Factors:
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for PAD. Smoking damages the arteries and accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing PAD. High blood sugar levels can contribute to arterial damage.
- Age: PAD becomes more prevalent with age. The risk increases significantly in individuals over the age of 50.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Elevated blood pressure can contribute to the hardening and narrowing of arteries, increasing the risk of PAD.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein) can contribute to the formation of arterial plaques.
- Genetics (Family History): A family history of PAD or atherosclerosis increases the likelihood of developing the condition.




.webp)