Deep Vein Thrombosis: Understanding the risks, causes and treatments
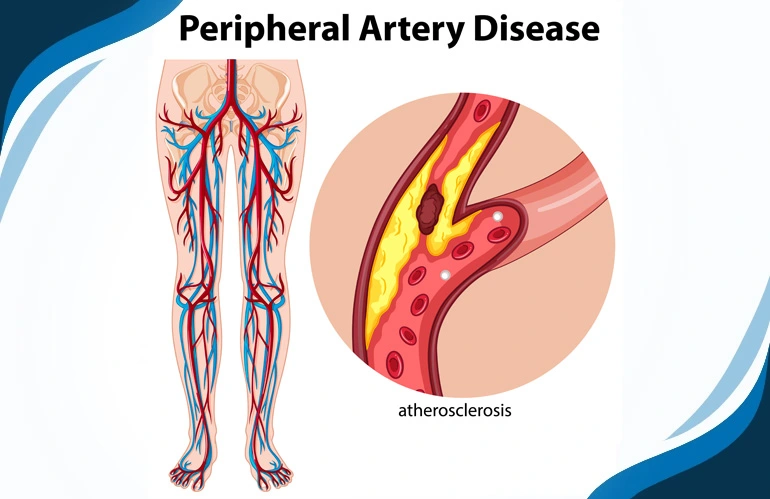
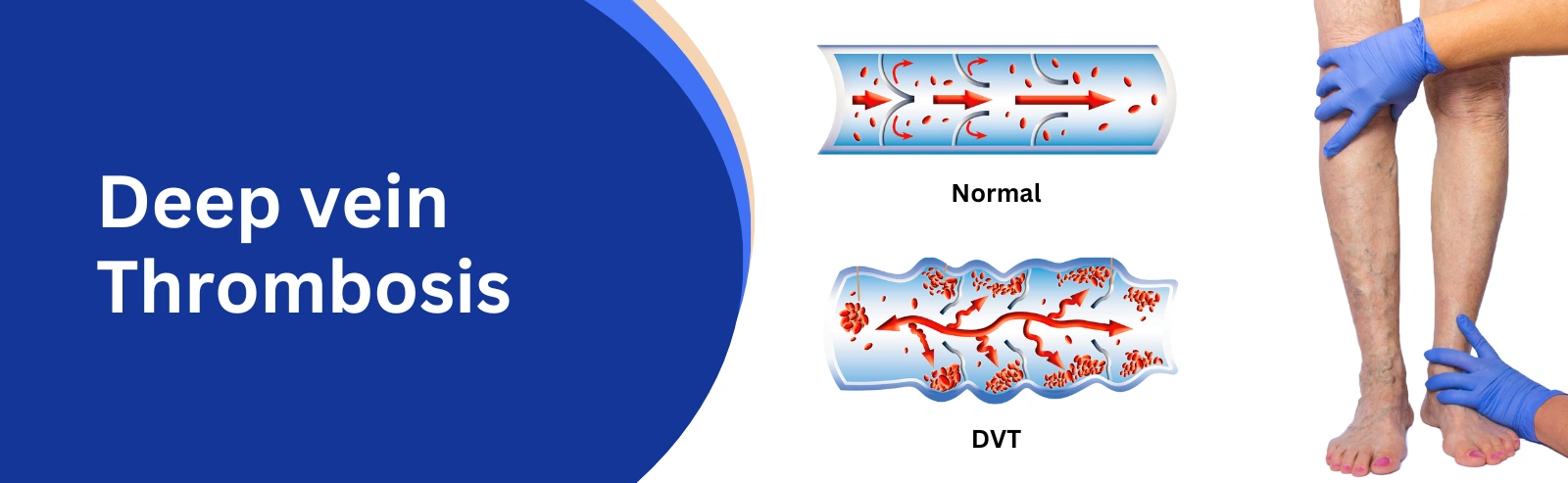
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), is a semi-emergency medical condition characterized by the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) within a deep vein, usually in the leg and thigh. Deep veins are the larger veins that are located deeper within the body.

How does DVT happen?
The process of DVT formation is influenced by various factors. Here's a general overview of how DVT happens:
Blood Clot Formation: Blood clots can form for various reasons, and the coagulation process is a normal part of the body's response to injury or damage. There are a number of anticoagulation factors and pro-coagulation factors in the blood and tissue. These factors are in balance to prevent unwanted blood formation and to form clots whenever required, as in situations of injury where bleeding needs to be stopped. The following conditions play a role in clot formation:
Stasis of Blood Flow: One of the key contributing factors to DVT is the slowing or stasis of blood flow. This can occur due to prolonged immobility, such as during long flights, bed rest, or extended periods of sitting at a desk. When blood flow slows down, especially in the deep veins of the legs, there is an increased risk of clot formation.
Injury or Trauma:Injury or trauma to the blood vessels can trigger the coagulation process by releasing pro-coagulation factors (as a part of normal physiological response to prevent bleeding). This can happen with surgery, fractures, or other types of damage to the blood vessel walls.
Hypercoagulability: Conditions that make the blood more prone to clotting, known as hypercoagulability, can contribute to DVT. This can be caused by genetic factors, certain medical conditions, or medications like OCP (oral contraceptive pills) or with hormone replacement therapy.
Who is at risk for DVT?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT). Some individuals may have a higher predisposition due to a combination of factors. Common risk factors for DVT include:



.webp)